Mesothelioma
Patients who have mesothelioma may be eligible for clinical trials to test the future treatments. They could also receive chemotherapy, radiation therapy and surgery.
mesothelioma lung might order a biopsy. This involves taking a small portion of tissue and examining the tissue under a microscope for cancer cells.
Based on the type tissue, mesothelioma can be divided into three types: epithelial (most frequent) and Sarcomatoid (second most prevalent) and biphasic. Epithelial mesothelioma is the most prevalent type and has a better survival rate than the other two types.
What is mesothelioma?
The mesothelium is a hefty membrane of protection that covers organs in the body. The lung's pleura is the most frequent site for mesothelioma, but it can be found in the diaphragm or the peritoneum, as well as in the heart sacs. It is uncommon to find mesothelioma in other parts of the body.
It is often difficult to identify mesothelioma as the tumors could look similar to other cancerous cells. A doctor might request fluid samples as well as a CT scan or an MRI to get more information about the cancer. These tests will assist doctors determine the stage of mesothelioma which can affect survival rates.
Patients diagnosed with pleural mesothelioma live longer than those diagnosed with mesothelioma peritoneal. However, pleural mesothelioma is more aggressive and grows faster than peritoneal mesothelioma, making it more difficult to treat.
The pleura is the thin layer of tissue that surrounds the chest cavity and lungs, as well as other organs within the abdominal cavity and thoracic cavity. A pleural mesothelioma tumour can affect the lung's lining and cause symptoms such as dry cough. It may also affect other organs in the thoracic region like the heart, causing pain when breathing or cardiac problems.
The symptoms of mesothelioma may range from mild to severe and may change depending on the stage of the cancer. Patients may experience swelling, difficulty breathing, and fever. Other symptoms include weakness and fatigue.
Mesothelioma treatment options vary based on the type and stage of the cancer as well as a patient's general health. The most commonly used treatments include surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Multimodal therapy is a combination of all three.
Most of the symptoms of pleural melanoma are located in the lining of the lung. More than 60% of mesothelioma patients experience chest discomfort. It can also lead to swelling of the lungs that could cause breathing problems. It can also cause swelling and pain in your abdomen. In addition to chemotherapy and surgery the patient may also undergo radiation to relieve pain or kill cancer cells after treatment.
Symptoms
When asbestos fibers are breathed in, they can irritate the lining of the lungs (pleura) and then spread to other areas of the body. This may affect the abdominal lining (peritoneum) as well as the heart (apex) and testicles (the tunica vaginalis). Mesothelioma cells vary, depending on whether they're composed of sarcomatoid or epithelial cells, and also the location where cancer begins to develop. These factors can affect how quickly it spreads to other tissues, as well as what symptoms patients experience.
The symptoms can manifest 10 to 50 years after asbestos exposure. Patients with pleural msothelioma usually experience chest pain, fatigue and difficulty breathing. As the tumor expands, it can cause swelling and a bloated feeling in the abdomen. Patients with peritoneal msothelioma can experience abdominal pain, fatigue, and loss of appetite.
The first step in identifying mesothelioma begins with a physical examination. A doctor will ask about your job and health history and check for indications of mesothelioma for example, a cough that does not disappear or chest pain. A doctor may require imaging tests, such as X-rays, CT scans and MRIs to detect growths or other changes in the chest or abdomen.
PET scans utilize a substance that binds cancer cells. The scanner then takes images of your body and shows the areas that absorb the compound more than normal tissue. This helps doctors identify mesothelioma cancer cells and target those areas for further analysis.
Blood tests can also help detect mesothelioma. They may reveal elevated levels of certain chemicals released by mesothelioma cancer cells. Additionally, doctors can measure how much fluid is building up in the lungs, and the amount of calcium in the lining of the lungs and diaphragm.
Other tests include a chest CT scan as well as biopsy, which is taking a small piece of tissue to test for mesothelioma cells under microscope. Additionally, some patients may try complementary and alternative treatments, such as massage therapy, acupuncture, or mind-body therapies to help manage their mesothelioma symptoms. A multidisciplinary team should oversee any treatment.
Diagnosis
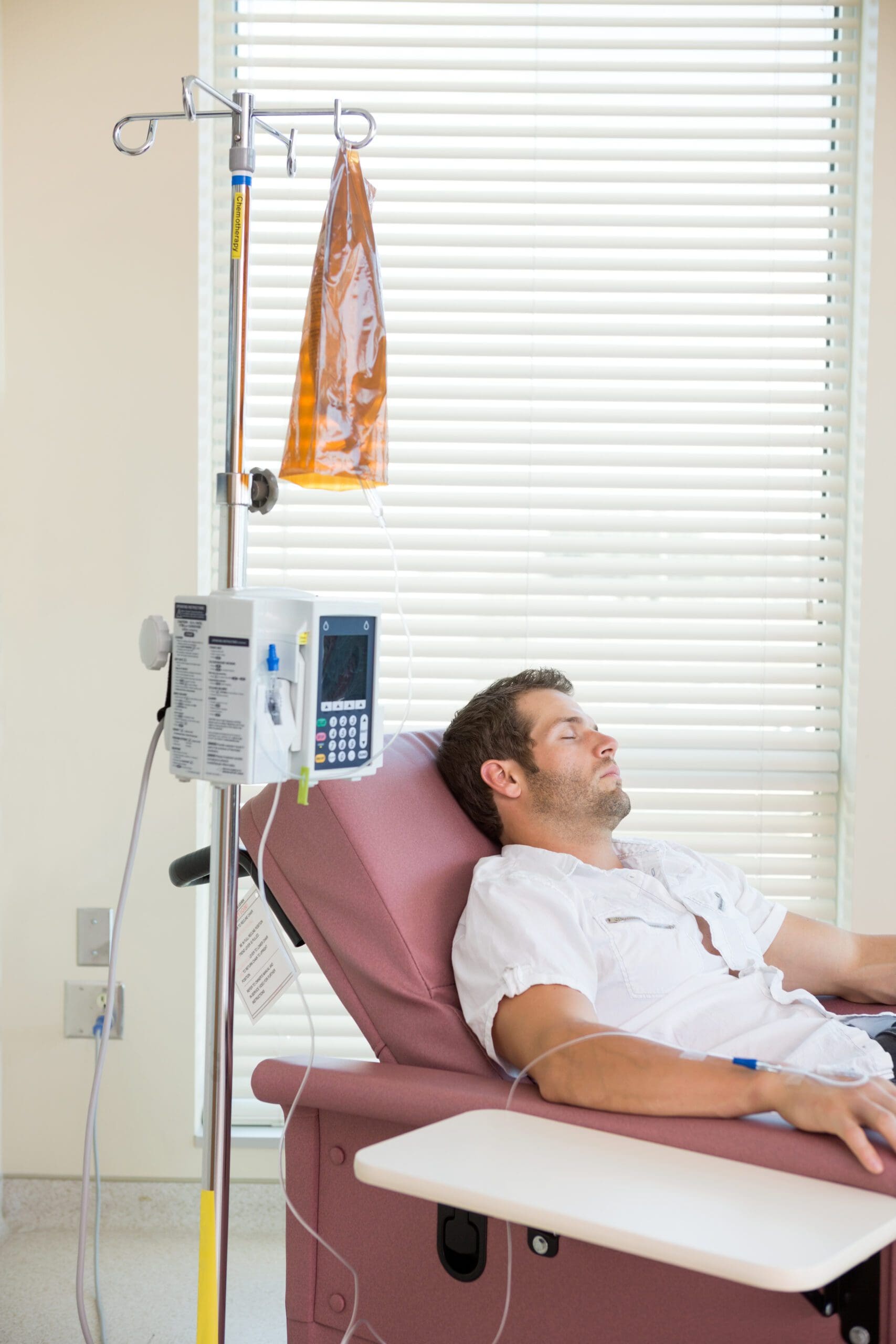
A lot of people suffering from mesothelioma have not diagnosed at the time of diagnosis. This is because the symptoms may be similar to common illnesses, such as the flu or pneumonia. As well, asbestos-related diseases can require a long time to manifest symptoms. By the time mesothelioma has been diagnosed, it is usually in the final stages of the disease, and more difficult to treat.
A doctor will begin with a physical exam and ask about symptoms and exposure to asbestos. They will also go through medical records to determine the type of mesothelioma and its stage. The type of mesothelioma that is diagnosed will determine the type of treatment.
Doctors make use of imaging scans in order to detect abnormalities and tumors. A X-ray scan can reveal a Pleural effusion (fluid inside the lungs) and other indications of mesothelioma. A CT scan or MRI offers more detailed images of the chest and abdomen. In some cases, doctors may use the PET scan to detect cancer cells that do not appear on the image.
A biopsy is the most reliable way to confirm the diagnosis of mesothelioma. A doctor will make use of a long, thin needle to take tiny pieces of tissue from the suspected site. It is not necessary to undergo surgery or hospitalization. A doctor will numb the area with medicine before performing the biopsy. In rare cases doctors may have open surgery if they can't reach the site with a needle or if the mesothelioma is too advanced for the biopsy.
Blood tests can also help confirm a mesothelioma diagnoses. They can detect levels of certain proteins that are elevated in mesothelioma patients.
A specialist in mesothelioma can interpret these and other test result. The specialist will then discuss the best option for your treatment.
A Pulmonologist is a specialist who specializes in lungs. Oncologists administer chemotherapy, and surgeons may operate on the abdomen or lungs to treat mesothelioma. They can also discuss with you about palliative treatment, which can enhance the quality of life by relieving symptoms such as pain, nausea and fatigue.
Treatment
It is important to work closely with your medical team once you are diagnosed with mesothelioma. This can include doctors, nurses and other specialists. The goal of mesothelioma treatment is to stop the cancer from spreading or returning for as long as possible, and it may also include treatments to alleviate symptoms like breathing problems and pain.
Doctors will design a custom treatment plan for each patient. The plan will be based on the kind of cancer and its location. The doctor will use different treatments to get the best results.
The first step in mesothelioma therapy involves the procedure of a biopsy. This procedure uses surgery or needles to remove a small portion of mesothelioma tissue to examine under microscopes for cancerous cells. Doctors may also order other tests, including imaging scans, such as the CT scan or MRI and blood tests to check for high levels of certain substances that may be a sign of mesothelioma. For instance, mesothelin-related, soluble peptides as well as fibul.
It is not uncommon to feel shocked or upset regarding a mesothelioma diagnosis especially when it is at an advanced stage. It is normal to experience these emotions and it can be helpful to seek support from family members, friends, or a mesothelioma group. It is important to learn the most you can about mesothelioma and consult a physician who is experienced in treating mesothelioma.
There are many types of mesothelioma that can be surgically removed. Doctors often combine surgery with other treatments, including chemotherapy and radiation therapy. They can administer chemotherapy prior to or following the operation. They might also add drains in the pleura to allow the fluids around the lungs to be cleared at least once a week.
In certain cases, the cancer could develop a recurrence. The doctor will recommend an aggressive procedure such as P/D or EPP in order to prevent the spread of tumors. Other patients may undergo maintenance therapy to keep the mesothelioma in remission for a period of months or even years. A few examples of these treatments are immunotherapy, and a drug that targets mesothelioma cells of sarcomatoid, which are the most difficult to treat.
